Staphylococcus aureus resistente a la meticilina (MRSA Fotografía de stock Alamy
A Staphylococcus aureus resistente à meticilina (SARM) é um tipo de bactéria Staphylococcus aureus (estafilococos) que é resistente a antibióticos beta-lactâmicos. Ela é contagiosa e pode causar infecção com risco de vida. SARM não é encontrada no ambiente natural (solo ou água). Ela vive no nariz e na pele de seres humanos, é.
Free picture methicillin, resistant, staphylococcus aureus, infections
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In children in the United States, most deaths associated with influenza tend to result either from an exacerbation of an underlying medical condition or invasive coinfection from another pathogen. As the percentage of children colonized with MRSA has increased, this bacterium has assumed a.
Mrsa o staphylococcus aureus resistente a la meticilina, imagen conceptual médica. Foto Premium

Prevenção e Controlo de Colonização e Infeção por Staphylococcus aureus Resistente à Meticilina (MRSA) nos hospitais e unidades de internamento de cuidados continuados integrados ( Direção-Geral da Saúde, 2015; Spain. Surveillance and control of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Spanish hospitals. Consensus document.
Staphylococcus aureus Murray Brown Labs
Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus and CA-MRSA in special populations. An important facet of the epidemiology of S. aureus is the fact that these bacteria infect "special populations". This term refers to population strata that can be differentiated based on ecological pressures and/or specific conditions of morbidity, such as the elderly, bedridden patients and patients with chronic.
PPT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS RESISTENTE A METICILINA SARM MRSA PowerPoint Presentation ID5787897

Based on the antibiotic susceptibilities, Methicillin resistance in S. aureus is defined as an oxacillin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of greater than or equal to 4 micrograms/mL. MRSA infection is one of the leading causes of hospital-acquired infections and is commonly associated with significant morbidity, mortality, length of stay, and cost burden. MRSA infections can be further.
FileHospitalassociated Methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Bacteria.jpg
_Bacteria.jpg)
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive bacterium commonly associated with severe infections in hospitalized patients.S. aureus produces many virulence factors leading to local and distant pathological processes. Invasiveness of S. aureus generally induces metastatic infections such as bacteremia, infective endocarditis, osteomyelitis, arthritis, and endophthalmitis.
Staphylococcus aureus meticilino resistente MRSA LABORATORIO VETERINARIO PATVETEC

Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature. First identified in purulent fluid from a leg abscess by Ogston in the 1880s and formally isolated by Rosenbach not long after, Staphylococcus aureus is well adapted to its human host and the health-care environment 1. S. aureus is both a frequent commensal and a leading cause of endocarditis, bacteraemia, osteomyelitis and skin and.
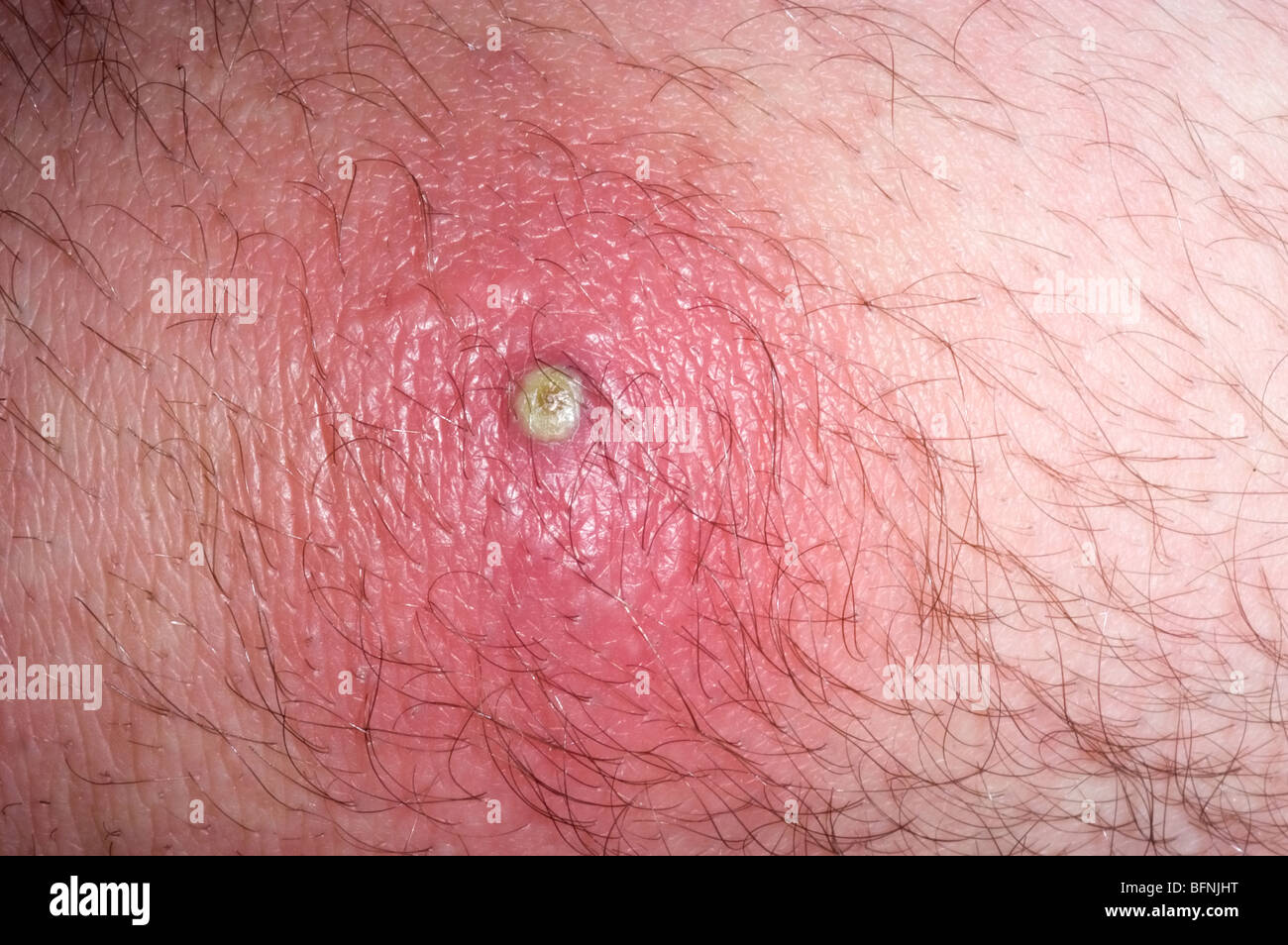
Staphylococcus aureus resistente a la meticilina (SARM) infección de la piel en un varón de 26
Strategies to monitor and control the spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections are dependent on accurate and timely diagnosis of MRSA in both hospital and community settings. In Latin America, significant diversity in diagnostic and susceptibility testing procedures exists at the regional, national and local levels.
Methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus — tissue, bacterial pathogen Stock Photo 160563784
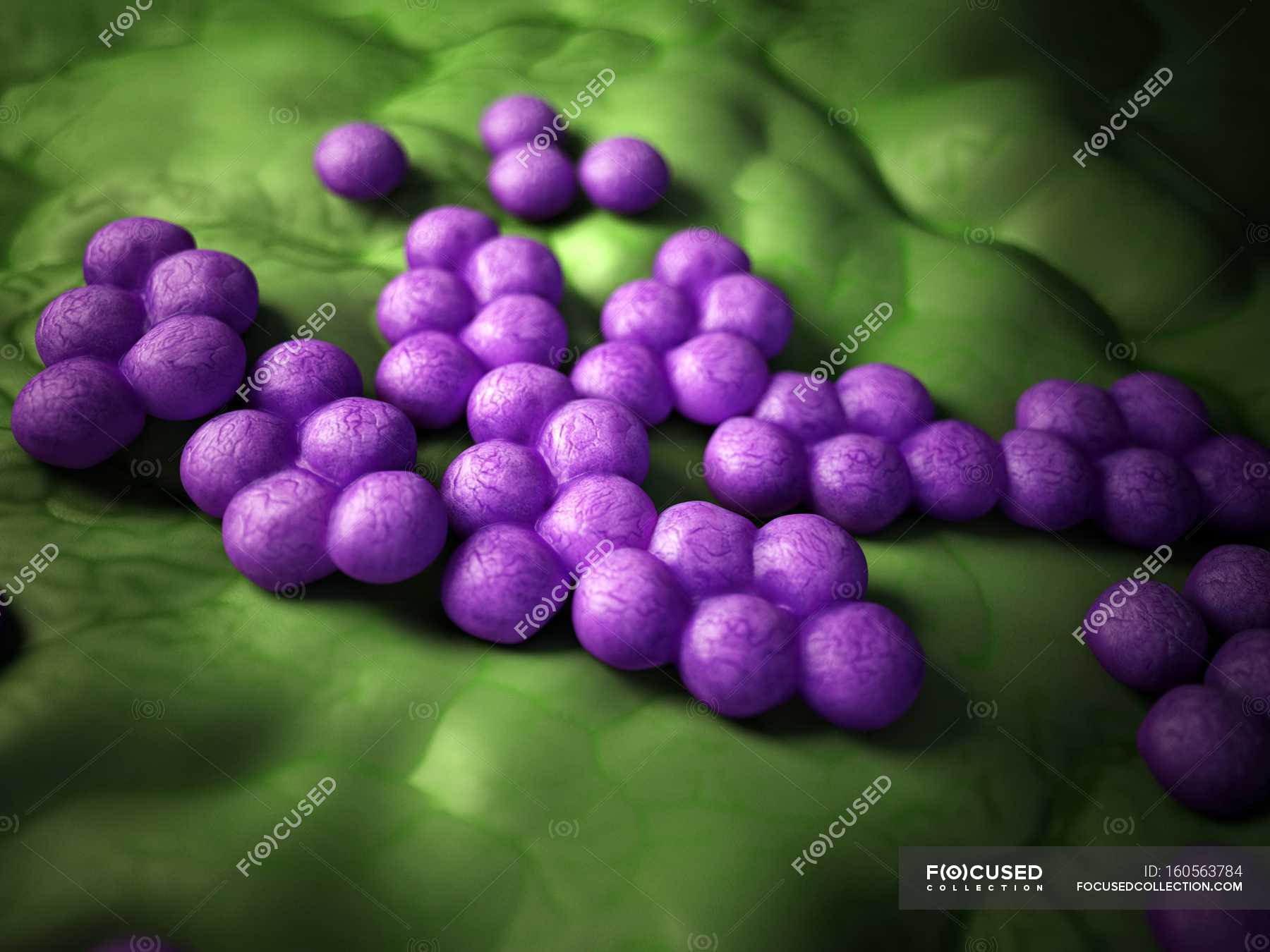
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a strain of pathogenic bacteria that is a major problem in the world's health. Due to their frequent interaction with humans, pets are one of the main risk factors for the spread of MRSA. The possibility for zoonotic transmission exists since frequently kept dogs and cats are prone to contract MRSA and act as reservoirs for spreading MRSA.
Epidemias Virais e Superbactérias Staphylococcus aureus meticilina resistente
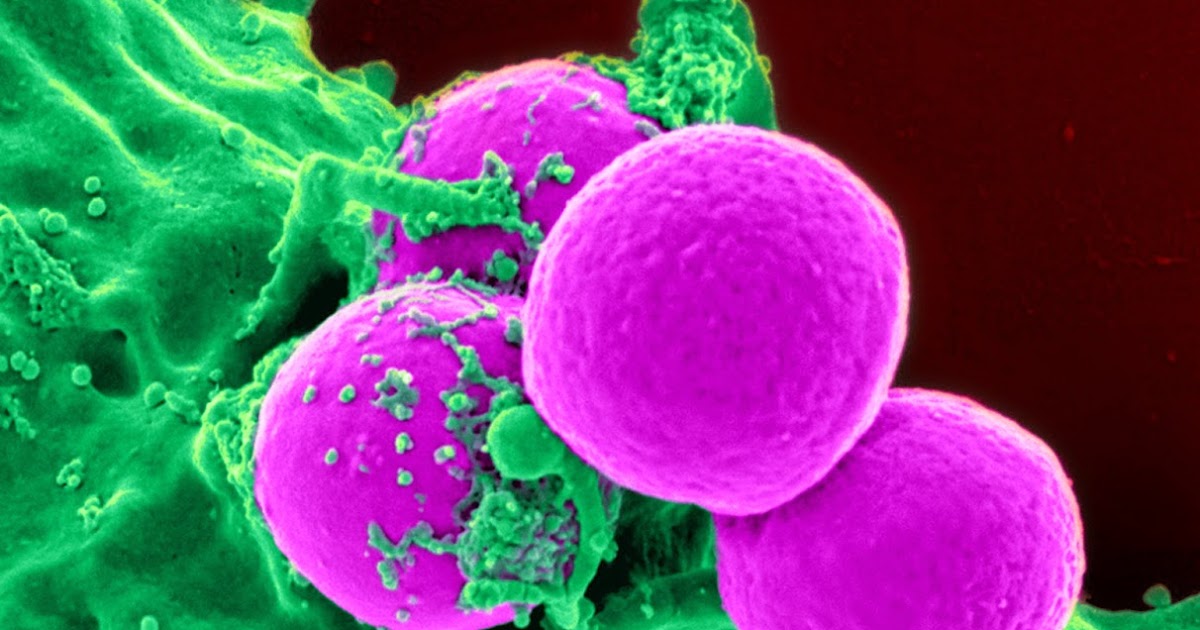
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of the most successful modern pathogens. The same organism that lives as a commensal and is transmitted in both health-care and community settings is also a leading cause of bacteraemia, endocarditis, skin and soft tissue infections, bone and joint infections and hospital-acquired infections.
Sintético 100+ Foto Staphylococcus Aureus Resistente A La Meticilina El último

The burden of disease from meticillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections is high. Around 100 000 invasive MRSA infections occurred in 2005 in the United States, and the number of associated deaths was about 19 000—more than that for HIV. 1 The epidemiology of MRSA has changed recently—infections are no longer confined to the hospital setting, but also appear in healthy.
Bacteria Staphylococcus aureus resistente a la meticilina (mrsa Fotografía de stock Alamy
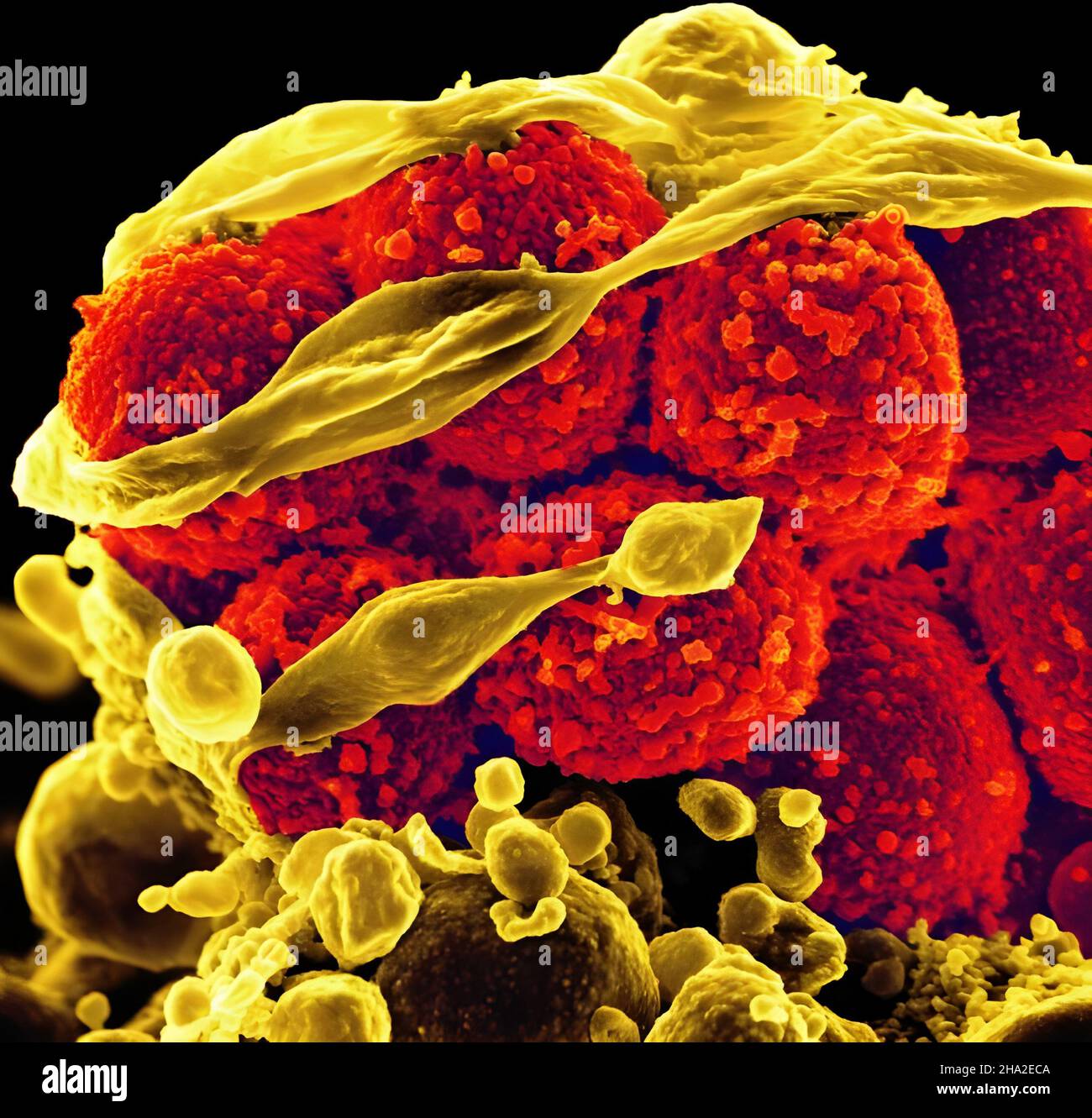
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a cause of staph infection that is difficult to treat because of resistance to some antibiotics. Staph infections—including those caused by MRSA—can spread in hospitals, other healthcare facilities, and in the community where you live, work, and go to school. You can help prevent.
Staphylococcus aureus resistente a meticilina (SARM) en un hospital de Traumatología. Factores

Since the 1960s, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has emerged, disseminated globally and become a leading cause of bacterial infections in both health-care and community settings.
Absceso y celulitis de MRSA Staphylococcus aureus resistente a la Meticilina mano infección en

Em poucos anos, o Staphylococcus aureus resistente à meticilina (MRSA) na pecuária se disseminou na produção de alimentos, com risco de infecção para os humanos. Os mais prejudicados são os criadores, trabalhadores de abatedouros e veterinários, que estão em frequente contato com animais portadores de MRSA ( 14 ).
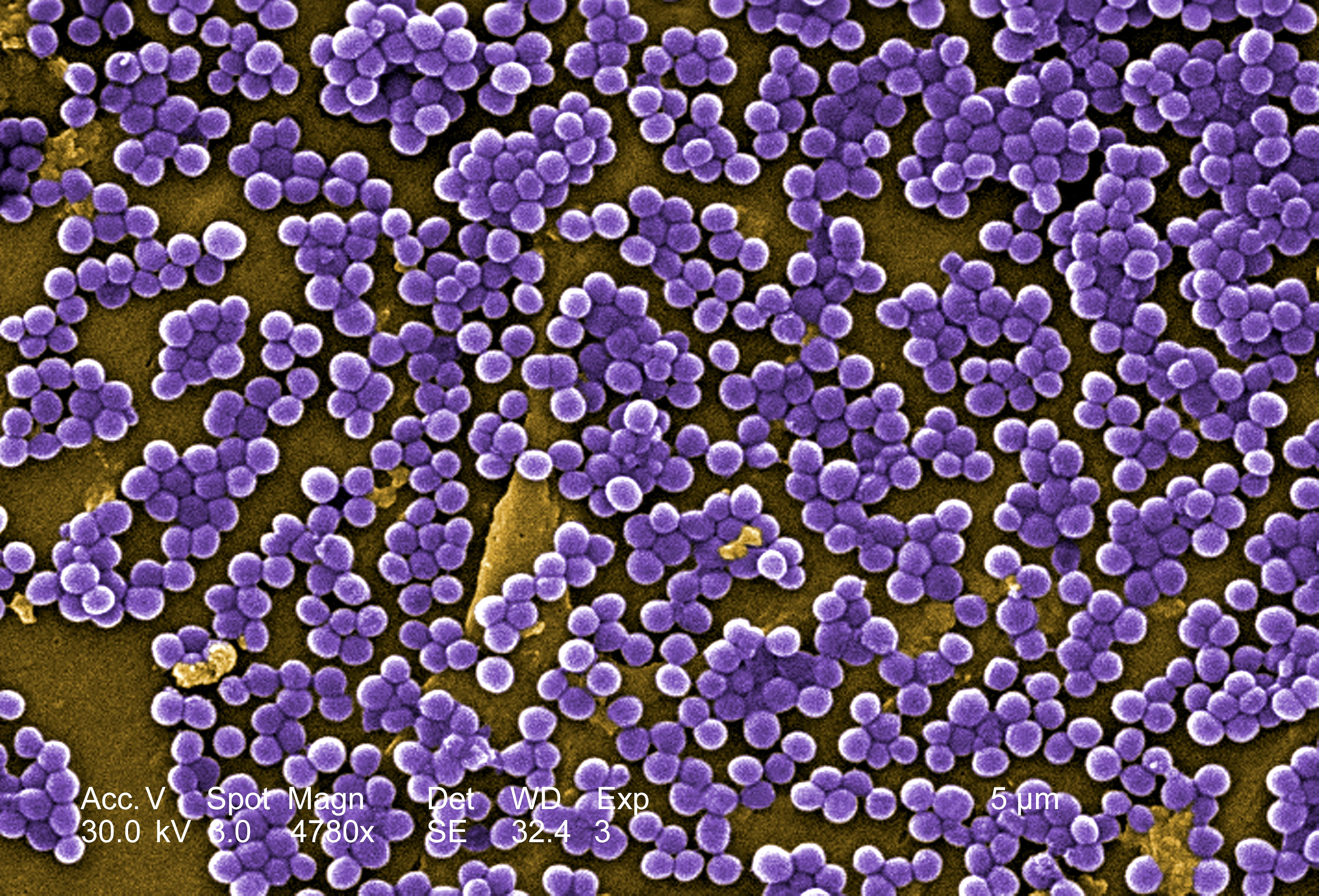
Staphylococcus aureus resistente a meticilina en microscopía electrónica de barrido (en purpura

An overview of basic and clinical MRSA research is provided and the expansive body of literature on the epidemiology, transmission, genetic diversity, evolution, surveillance and treatment of MRSA is explored. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of the most successful modern pathogens. The same organism that lives as a commensal and is transmitted in both health-care and.
Estafilococo aureus resistente a meticilina (sarm) o "superbug"

Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of the most successful modern pathogens. The same organism that lives as a commensal and is transmitted in both health-care and community settings is also a leading cause of bacteraemia, endocarditis, skin and soft tissue infections, bone and joint infections and hospital-acquired.